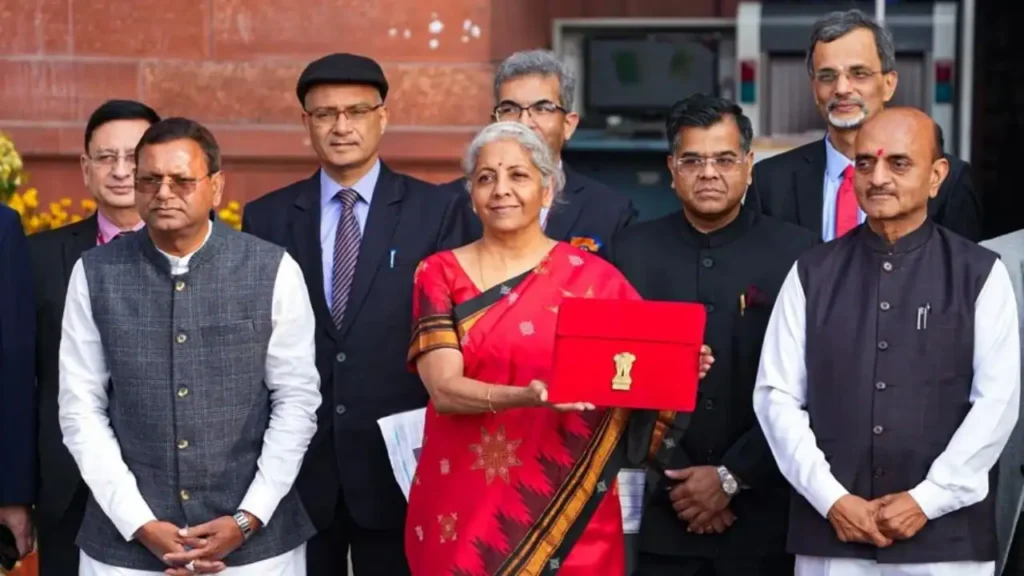
Budget 2026: Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman to Present Budget for the 9th Time; Faces These 9 Major Challenges

Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman is set to present the Union Budget 2026-27 on February 1, 2026. At a time when India has surpassed Japan to become the fourth largest economy in the world and is steadily moving towards becoming the third-largest within the next two years, the government faces several significant economic challenges. Here’s a look at the key hurdles the Finance Minister will need to address while presenting the budget:
1. Slowing GDP Growth
According to the Economic Survey, India’s GDP growth for FY 2026-27 is projected to be between 6.8% and 7.2%. While the government aims to make India a developed nation by 2047, sustaining a growth rate of 8% or more will be crucial to achieve this goal.
2. Continuous Rupee Depreciation
Despite RBI interventions, the Indian rupee remains under pressure. On January 29, 2026, the rupee hit an all-time low of 92 against the US dollar. Between April 2, 2025, and January 22, 2026, the rupee depreciated by nearly 6.5%.
3. Job Cuts in IT and Software Sector
The IT and software sectors are facing employment challenges. During the first nine months of FY 2025-26, India’s top five IT companies hired only 17 new employees, compared to 17,764 in the same period last year.
4. Rising Trade Deficit with China
India’s trade deficit with China continues to widen. China exported goods worth approximately ₹8.39 lakh crore to India, putting pressure on domestic industries.
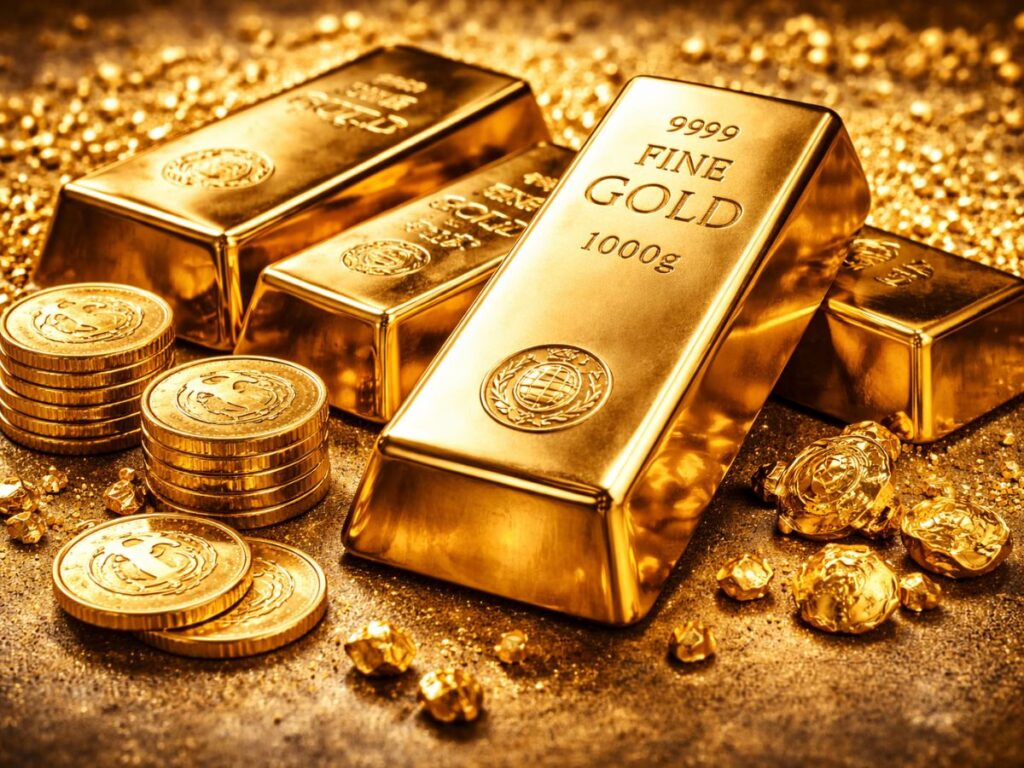
5. Record High Gold and Silver Prices
Gold and silver prices have reached historic highs. On January 30, 2026, gold was priced at ₹1.71 lakh per 10 grams and silver at ₹3.95 lakh per kg, impacting mainly the middle class, particularly in a country that sees roughly 1 crore weddings annually.
6. Air Pollution and Sanitation Concerns
According to CREA’s January 2026 report, 44% of Indian cities are grappling with chronic air pollution. In Delhi, out of 365 days, the air quality is considered “good” for only 79 days.
7. High Tariffs by the US
The United States has imposed a 50% tariff on Indian products, including a 25% base tariff and a 25% additional tariff, the latter imposed due to cheaper crude oil imports from Russia. This has adversely affected Indian exports.
8. Slow Growth in Manufacturing Sector
Despite the “Make in India” initiative, the manufacturing sector’s contribution remains stuck at 12.13% of GVA, while the government’s target is 25%.
9. Agriculture and Farmer Productivity
India’s food grain production for 2024-25 is estimated at 3,577.3 lakh metric tons, an increase of 254.3 LMT over the previous year. However, the yield of wheat, maize, soybean, and pulses is still below the global average. Experts suggest that improving farmers’ income requires a focus on productivity enhancements, quality seeds, modern technology, and efficient irrigation.


 English
English